Letters of Credit
A Letter of Credit (LC) is a financial document issued by a bank on behalf of a buyer, guaranteeing payment to the seller upon the fulfillment of specified conditions. It acts as a contractual agreement between the buyer, the seller, and the issuing bank, mitigating the risks associated with cross-border transactions
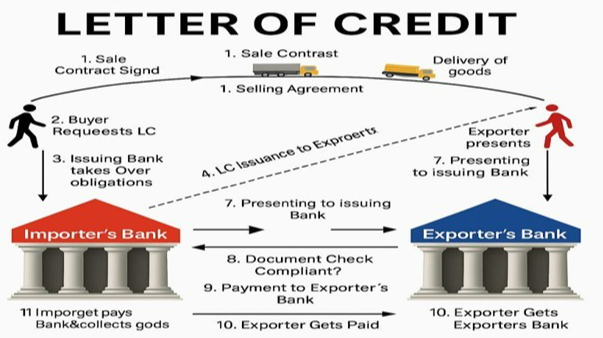
How it works
- Agreement: The buyer and seller agree on the terms of the sale and the use of a Letter of Credit (LC).
- Issuance: The buyer applies for an LC from their bank (issuing bank), which then issues the LC to the seller's bank (advising bank).
- Shipment: The seller ships the goods and provides the necessary documents (e.g., bill of lading, invoice) to the advising bank.
- Verification: The advising bank verifies the documents and forwards them to the issuing bank.
- Payment: Once the issuing bank confirms that the documents meet the LC terms, it releases the payment to the seller
Merits of Letters of Credit
- Security for Both Parties:
- For Sellers: Ensures payment if the terms of the LC are met, reducing the risk of non-payment
- For Buyers: Guarantees that payment will only be made if the seller fulfills the terms of the contract
- Facilitates International Trade:
- Reduces the risks associated with cross-border transactions, such as differing laws and geographical distances
- Customizable:
- LCs can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the buyer and seller, including terms and conditions
- Improves Cash Flow:
- Ensures timely payments, which can enhance cash flow management for both parties
- Creditworthiness:
- Acts as a credit certificate for the buyer, demonstrating their ability to pay
Comparison with other Payment Terms
- Advance Payment:
- Pros: Immediate payment before shipment.
- Open Account:
- Pros: Goods are shipped and delivered before payment is due
- Documentary Collection:
- Pros: Banks handle the exchange of documents and payments.
Conclusion
Letters of Credit provide a secure and reliable payment method for international trade, offering protection and assurance to both buyers and sellers. While they can be more complex and costly compared to other payment terms, their benefits in mitigating risks and ensuring smooth transactions make them a preferred choice in global trade.
